| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
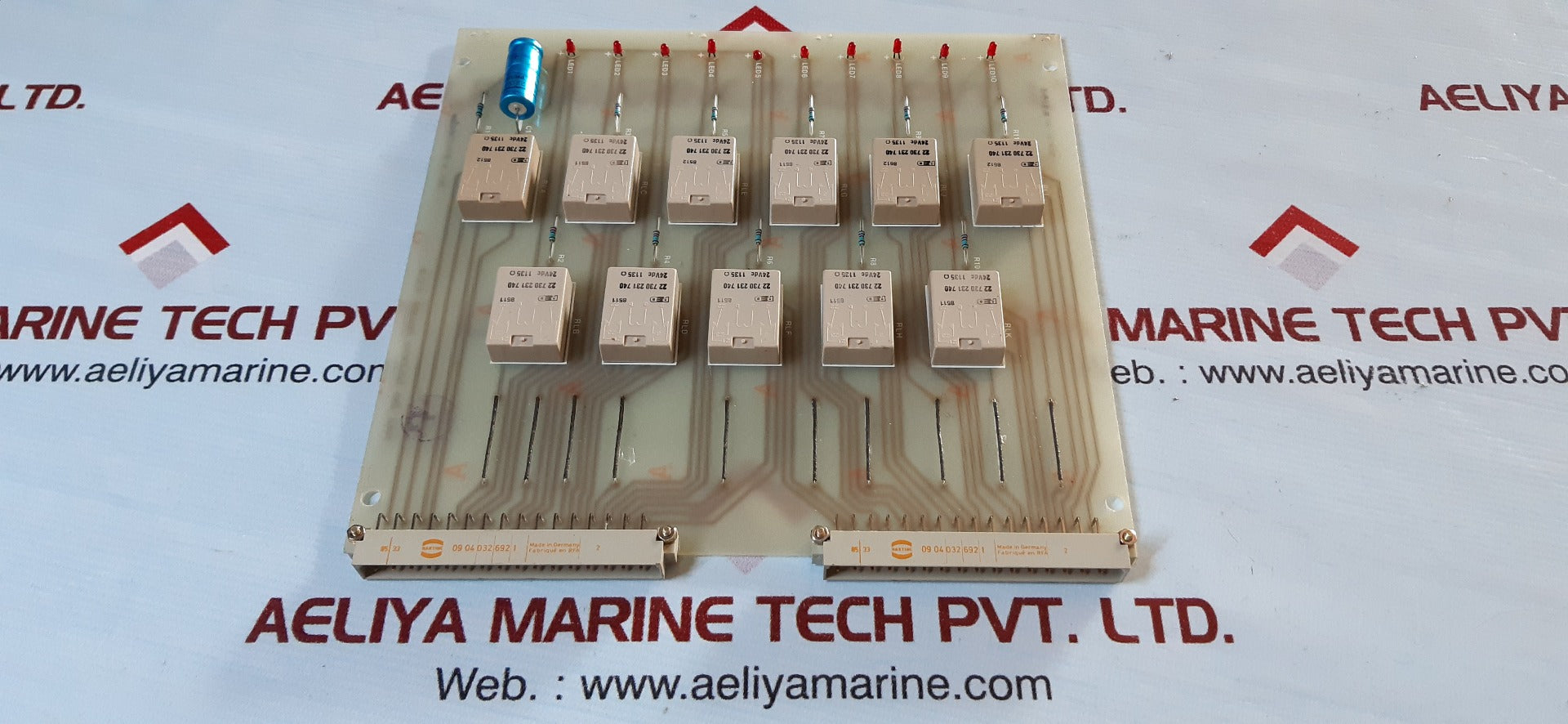
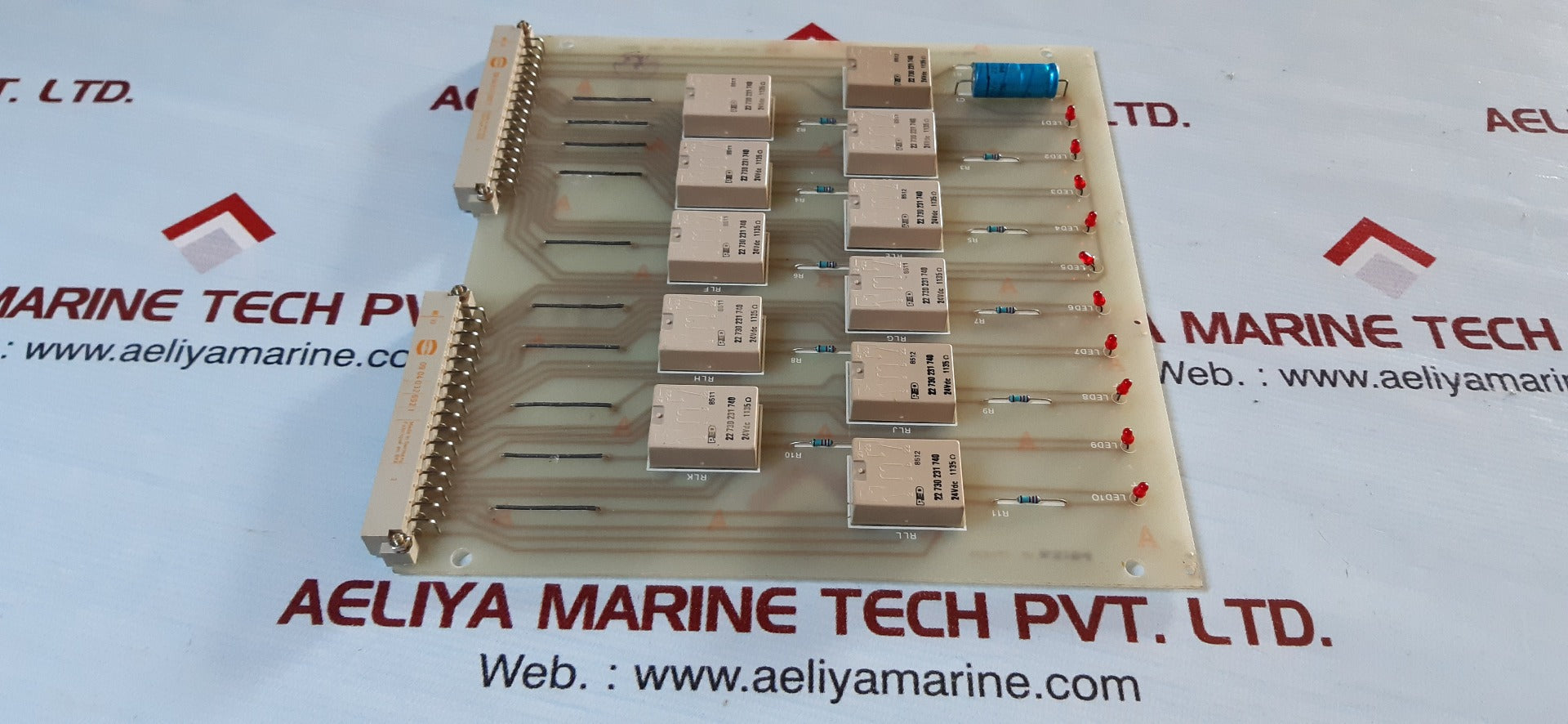
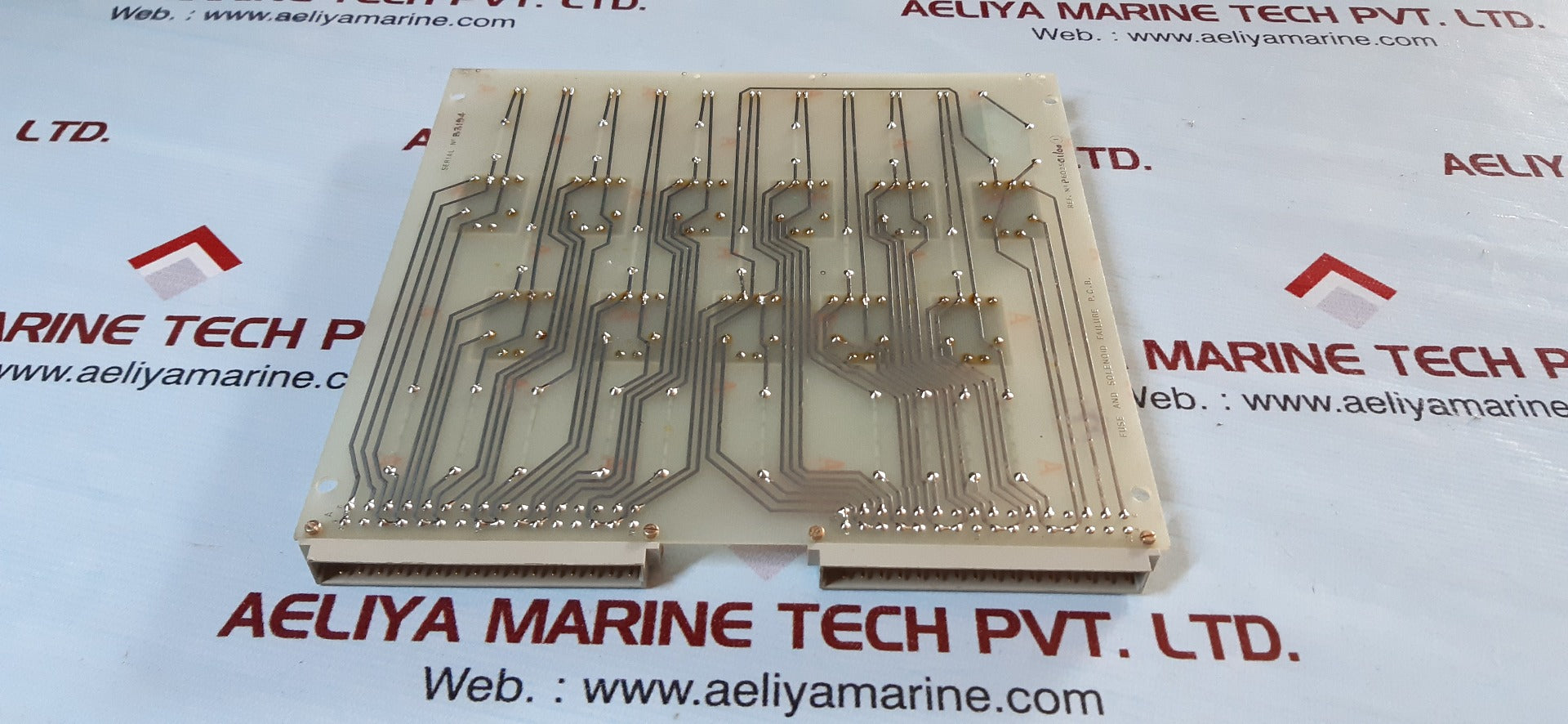
| Issue | Fuse and Solenoid Failure |
| PCB Card | P602501/00 |
| Abbreviation | P.C.B. |
Understanding the P602501/00 PCB Card
The P602501/00 PCB card is a critical part of industrial equipment, automation, and electric control units. It distributes power and controls major components such as solenoids, relays, and other components.
When a fuse or solenoid melts on this board, it will result in system breakdowns, functionality loss, or even catastrophic failure of the system.
Common Reasons for Fuse and Solenoid Melting
1. Short Circuits or Overcurrent
Fuses guard against circuits by rupturing the link when there is excessive current passing through.
An overload caused by a short circuit will blow the fuse instantly.
2. Voltage Spikes & Power Surges
Excessive voltage fluctuations will burn fuses and destroy solenoids.
This usually results from unstable power supply or malfunctioning wiring.
3. Solenoid Coil Overheating
Extended operation without adequate cooling will lead to burnout of the solenoid coil.
Inadequate ventilation, grime accumulation, or extended high-load operations may exacerbate the problem.
4. Mechanical Wear and Tear
Solenoids have moving components that wear out over time.
Cycles of repetitive activation can result in worn or jammed plungers, which lead to failure.
5. Moisture & Corrosion
Humidity or liquid exposure can corrosion the PCB and short out components.
Moisture entry can result in deterioration of solenoid coils and rusted connectors.
6. Manufacturing Defects
Inadequate soldering, poor PCB traces, or substandard components lead to early failures.
Factory faults may result in surprise fuse blowouts or inadequate solenoid operation.